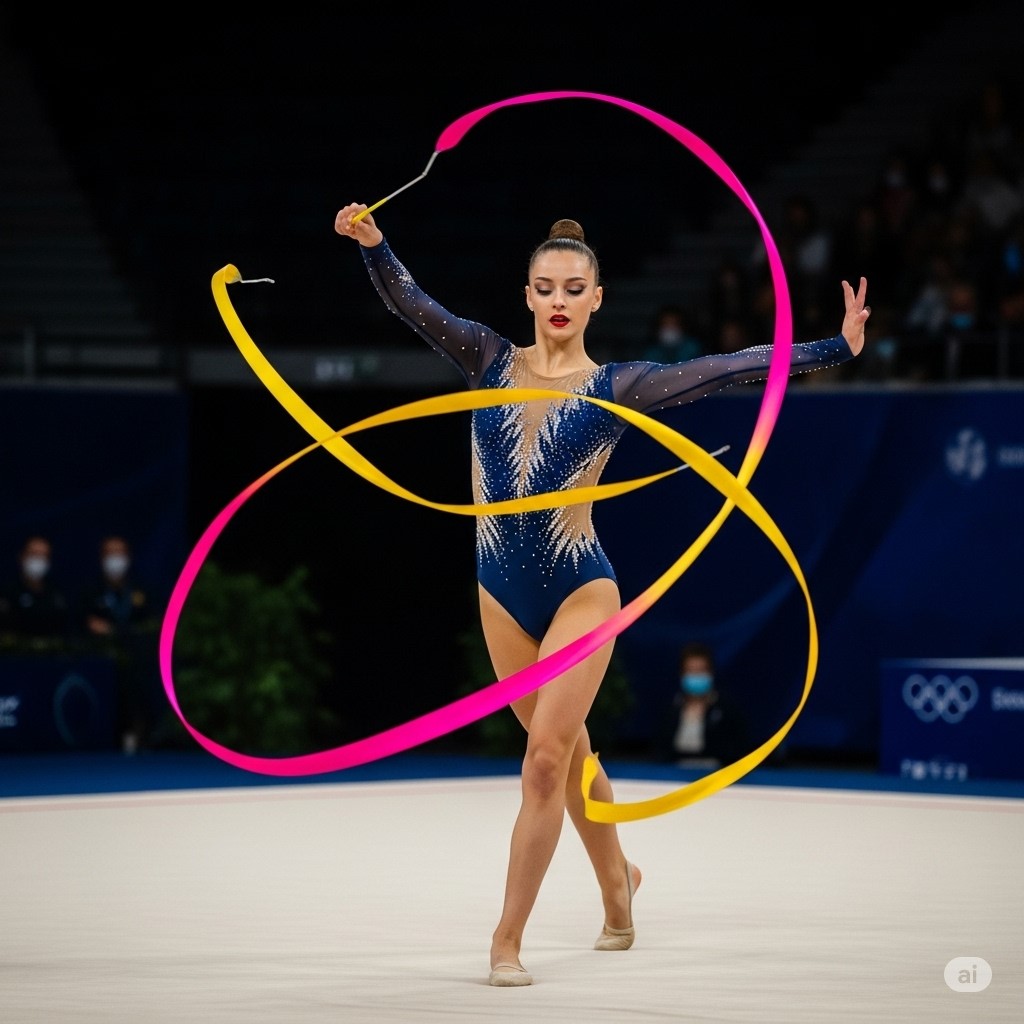
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics: A Beautiful Blend of Art and Athleticism
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics is one of the most visually captivating sports in the world. This discipline combines grace, coordination, athleticism, and creativity. In this blog post, we will dive into the origin, history, global popularity, rules, and current amateur and professional scenes. We’ll also explore the political and social significance of this elegant yet demanding sport.
The Origin and History of Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics
The origins of Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics date back to the early 20th century. This sport evolved from a mix of ballet, gymnastics, and theatrical dance. It was first practiced in Eastern Europe, particularly in Russia. Influences from Swedish and German gymnastics methods also shaped its early form.
In the 1940s, rhythmic gymnastics began to formalize as its own discipline. The Soviet Union played a significant role in shaping and promoting it. In 1963, the first world championships were held in Budapest. The International Gymnastics Federation (FIG) officially recognized the sport in 1961.
The ribbon was introduced as one of the five apparatus used in rhythmic gymnastics. This inclusion gave birth to the unique branch known as Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics. Athletes started to train with long, flowing ribbons attached to sticks, combining dance with gymnastic technique.
Since then, the sport has grown steadily. In 1984, rhythmic gymnastics debuted at the Olympic Games in Los Angeles. Ribbon routines have since become a staple event in international competitions.
Global Popularity of Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics enjoys strong popularity in several countries. Russia, Bulgaria, and Ukraine consistently produce top gymnasts. These nations invest heavily in training and youth development.
Asian countries like China, Japan, and South Korea also excel. Their athletes bring precision, discipline, and innovative choreography. The sport is featured prominently in their national and regional competitions.
In Western Europe, countries like Spain, Italy, and France have thriving rhythmic gymnastics communities. Canada and the United States also maintain a solid presence in the sport.
Latin American countries, including Brazil and Mexico, are catching up fast. They have been increasing investments in gymnastics infrastructure and coaching.
Globally, Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics is broadcast during major events. The Olympics, World Championships, and World Cups draw millions of viewers. This visibility helps grow the fan base and inspires young athletes.
Youth and Amateur Participation Worldwide
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics is widely taught in schools and local clubs. It provides young athletes with an artistic yet athletic outlet. Most countries have structured programs that introduce the sport at an early age.
In Russia and Ukraine, children begin training as young as five. National academies scout talent through school competitions and community clubs. These academies focus on technique, musicality, and discipline.
Japan and China also have rigorous youth systems. Their school-based programs are highly organized. Students compete at local, regional, and national levels.
In North America and Western Europe, clubs form the backbone of youth development. Coaches focus on fun, fitness, and foundation skills. Children gradually advance to competitive routines.
Youth tournaments and local meets help amateur athletes gain confidence. Many schools include rhythmic gymnastics in physical education programs. This exposure increases participation and awareness.
Non-profit organizations and sports associations frequently support amateur events. These competitions foster community and sportsmanship among young athletes.
Professional Leagues and International Events
While Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics does not have formal “leagues” like team sports, it boasts a structured international circuit. The FIG oversees global competitions such as the World Championships, World Cup Series, and Grand Prix events.
Top gymnasts from around the world compete in these events. They represent their countries and earn rankings based on performance. These rankings affect qualification for the Olympics and other major tournaments.
Russia remains dominant in professional rhythmic gymnastics. The country has produced numerous world champions and Olympic medalists. Bulgaria and Ukraine are also consistent contenders.
In Asia, China and Japan have developed professional teams. These athletes often train at national training centers and receive government support.
Some countries organize national rhythmic gymnastics leagues. These leagues support elite gymnasts and help them prepare for international competitions. Club-based systems often feature in-house tournaments and exhibitions.
Athletes gain sponsorship deals and media attention through international success. Professional gymnasts often perform in shows, galas, and festivals, bringing the sport to wider audiences.
Political and Social Significance
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics holds considerable political and social significance. In the Soviet era, the sport symbolized national pride and athletic excellence. Success in international events was used to showcase ideological superiority.
Even today, countries like Russia and China view rhythmic gymnastics as a soft power tool. International victories enhance national prestige and promote cultural values.
Socially, the sport empowers young girls and women. It promotes confidence, discipline, and physical fitness. Many programs emphasize teamwork and mutual respect.
Inclusion and diversity efforts have started to gain traction. Though historically female-dominated, male rhythmic gymnasts are slowly gaining recognition. Countries like Japan and Spain now support men in rhythmic competitions.
The sport also provides career paths beyond competition. Many former athletes become coaches, choreographers, or judges. Others work in performance arts or fitness industries.
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics has been used in community-building initiatives. It bridges cultural gaps through shared appreciation of movement and music.
Rules and Scoring System
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics follows specific rules set by the FIG. The apparatus consists of a ribbon attached to a stick. The ribbon must be at least six meters long for senior athletes.
Performances take place on a 13×13 meter floor. Routines last 75 to 90 seconds and must be performed to music. Gymnasts aim to synchronize their movements with the rhythm and melody.
The ribbon must remain in constant motion. Patterns like spirals, snakes, and throws are requirements. Athletes must demonstrate flexibility, balance, strength, and agility.
Judging is based on three main components: difficulty, execution, and artistry. Difficulty scores reflect the complexity of movements and combinations. Execution measures technical precision. Artistry evaluates musical interpretation, expression, and choreography.
You receive penalties for errors like knots in the ribbon, stepping out of bounds, or losing the apparatus. Precision and fluidity are essential for high scores.
In team events, groups of five athletes perform coordinated routines. Synchronization and group dynamics become critical. Group routines may involve exchanges and collaborations that increase complexity.
All routines are evaluated by a panel of judges. Scores are posted immediately after performances, adding excitement to competitions.
Equipment and Training
The ribbon used in Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics is made from satin or a similar material. It is light and designed to flow smoothly in the air. The stick is usually made of wood or plastic and must meet FIG specifications.
Athletes train extensively to master control over the ribbon. They practice patterns, throws, and catches repeatedly. Flexibility, strength, and stamina training are essential parts of daily routines.
Ballet and modern dance classes are common for rhythmic gymnasts. These classes enhance grace, posture, and musical interpretation. They also use mental focus and visualization techniques.
Nutrition and injury prevention are critical. Gymnasts follow strict regimens to maintain peak physical condition. Coaches and physiotherapists play vital roles in long-term athlete development.
Cultural and Artistic Impact
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics merges athletic skill with artistic expression. It compares to performing arts like ballet and modern dance. The music, costume, and choreography contribute to the sport’s visual appeal.
Audiences appreciate the creativity and elegance of ribbon routines. The sport is featured in cultural festivals and ceremonies. It brings beauty and emotion to athletic performance.
Many choreographers experiment with different music genres and themes. This variety keeps the sport fresh and engaging. Costumes always match routines, adding an extra layer of artistry.
Several documentaries and films have highlighted the lives of rhythmic gymnasts. These stories showcase dedication, sacrifice, and the joy of performance.
Future of Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics
The future of Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics looks promising. Increased media coverage and online content are attracting new fans. Social media platforms allow gymnasts to share their routines and training journeys.
International federations are investing in grassroots development. More countries are starting youth programs and coaching clinics. These initiatives aim to expand the sport’s global footprint.
Technological advancements are improving training methods. Trainers use video analysis, motion capture, and AI-assisted coaching tools. These tools help athletes refine technique and avoid injury.
There is a growing push for gender inclusivity. Mixed-gender events and male rhythmic gymnastics categories are gaining popularity. This expansion could redefine the sport’s future.
Olympic committees and global broadcasters continue to support the sport. With consistent growth and innovation, Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics will remain a fixture on the world stage.
Conclusion
Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics is more than just a sport. It is a celebration of movement, discipline, and creativity. From its origins in Eastern Europe to its global reach today, the sport continues to evolve.
Its impact is seen in youth development, cultural exchange, and international competition. Whether in school gyms or Olympic arenas, the ribbon dances on, telling stories through motion.
By understanding its history, rules, and significance, we gain deeper appreciation for Rhythmic Ribbon Gymnastics. This unique sport will continue to inspire generations to move with purpose and perform with passion.





